This Week’s Industry News
Compiled by the Rocket Clicks Team
Top Stories
How To Display Correct Date in Google Search Results
Google shared best practices to improve accuracy when it comes to Google Search deciding which date to display for your web page. Google has an automated system that determines when dates are relevant and/or important to include by looking at the date and time on a page or in structured markup. However, to ensure the correct date is chosen, Google suggests following these guidelines:
- Provide a clear, visible date:
- For Google News, date and time need to be included between the headline and the article text.
- Always use a current date; never use a future date or a date linked to an article’s event.
- Remove or minimize the use of other dates on the page to avoid confusion.
- Use the datePublished and dateModified schema with the correct time zone designator for AMP or non-AMP pages. When using structured data, make sure to use the ISO 8601 format for dates.”
- Include new date only for significant updates
- Don’t try to trick Google by updating the date after only minor changes.
- Don’t create a new page then redirect the old page to the new one. Just update the old page content and the date that article was published.
Source: Google Webmaster Central Blog
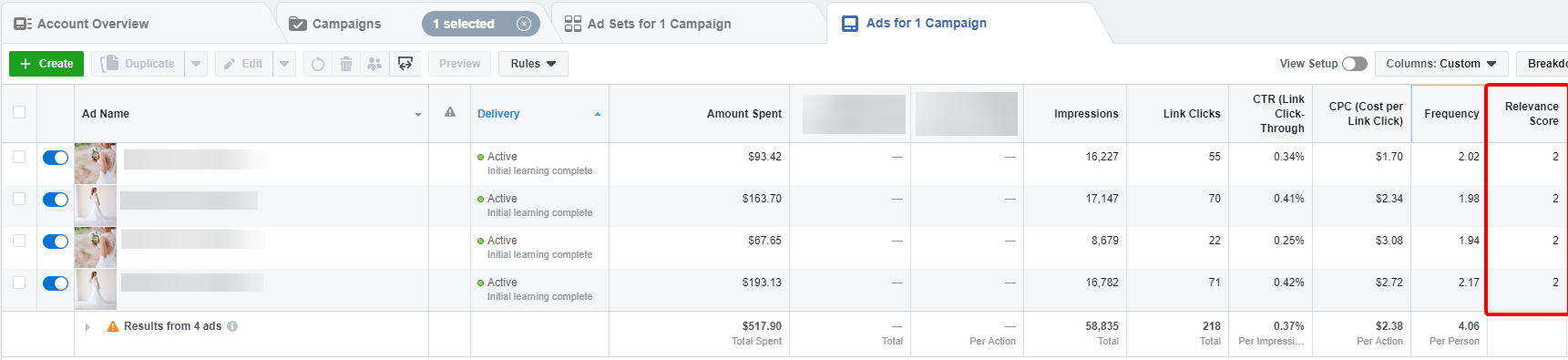
New Ad Relevance Measurements in Facebook
Facebook is replacing the single relevance score with 3 new relevance metrics. There will also be changes to how Facebook calculates the potential reach of ads. The 3 new metrics will be quality ranking which is an ad’s perceived quality compared with ads competing for the same audience, engagement rate ranking. how an ad’s expected engagement rate compared with ads competing for the same audience, and conversion rate ranking, how an ad’s expected conversion rate compared with ads that had the same optimization goal and competed for the same audience. The previous relevance metric will be removed on April 30. The potential reach metric will be updated to include only people who were shown an ad in the last 30 days. Previously, potential reach was estimated based on the number of total monthly active users on the network which didn’t factor in users who may not have been able to view the ads.
Source: Search Engine Journal
Google My Business Rolls Out New Onboarding Process
Google My Business is starting to roll out a new onboarding process for users to set goals when they create a new listing. Users can select up to six goals from the following list:
- Help customers discover my business
- Share updates with customers
- Learn how people find my business on Google
- Have accurate information on Google
- Respond to customers
- Promote my business online
Once the goals are selected, GMB will calculate a personalized action plan telling the user what to do next and what these action items will accomplish. Action item examples include: viewing performance reports, responding to reviews, and uploading photos. This new onboarding process began rolling out earlier this month, so it’s not available for everyone quite yet.

Photo courtesy of Search Engine Journal
Source: Search Engine Journal
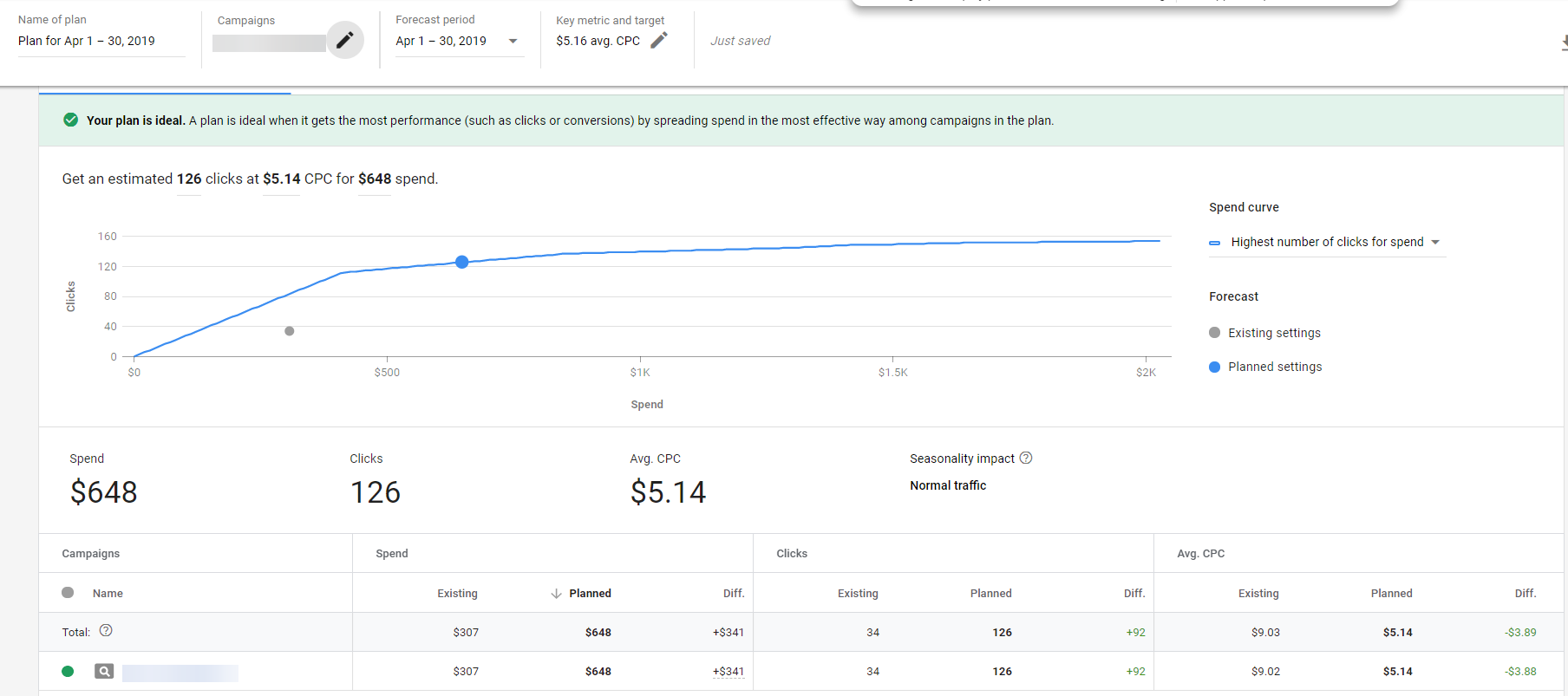
New Budget Planner Tool in Google Ads
Google is rolling out a new Budget Planner Tool. You can create a budget plan based on either clicks or conversions as a key metric. There is also the option to choose a target: clicks, spend or average CPC if you select clicks as the primary metric, or conversions, spend or average CPA when conversions is your key metric. If you choose a target, you can manually enter a target amount, or you can choose from “previous period” or the “same time last year.” Google will then generate a draft budget plan. The forecast chart will show a gray point showing how your campaigns are expected to perform with the existing settings if you make no changes. A blue line indicates how changes in spend will impact your key metric. You can toggle to see the spend curve based on different goals. Scuh as “highest number of clicks for spend” or “lowest average CPC for spend.”
Source: Search Engine Land
Analysis:
Step-by-Step Guide for Submitting Your Site for Indexing
Whether you have a new website or you’re just adding content, indexation is a critical step in becoming visible in search and having search engines find your content more efficiently. Here’s a step-by-step guide to easily submit websites and pages to search engines:
To submit an entire website, you’ll need to:
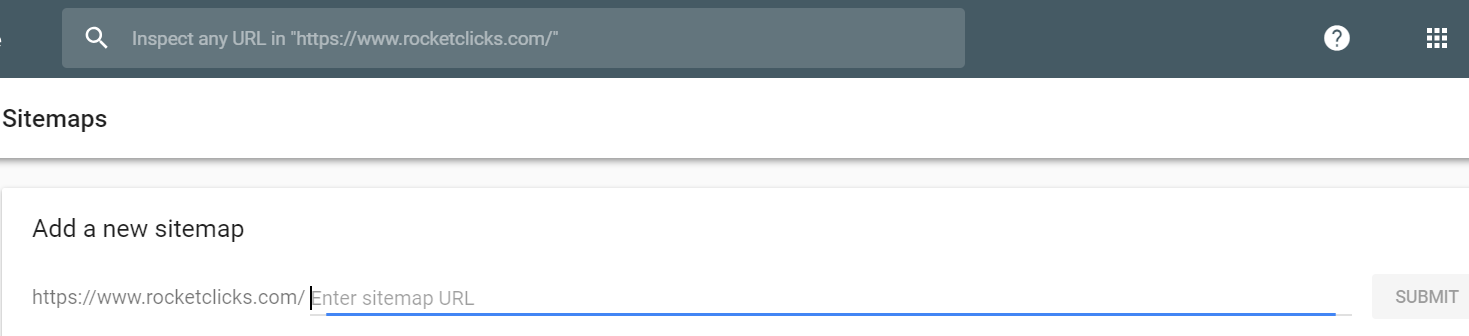
- Create an Optimized XML Sitemap – you can create smaller, categorized parts of your sitemap for images or blogs
- Test if it is uploaded correctly to your site by going to your site’s name with /sitemap.xml
- Add Link to Sitemap in robot.txt and Remove Disallow Directives – this will help search engines find your sitemap, and ensure that they can crawl your site
- Submit Individual Sitemaps or Sitemap Index to Google Search Console & Bing Webmaster Tools
To submit an individual page, you’ll need to:
- Request Indexing through Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool
- Use the ‘Submit URLs’ tool in Bing Webmaster Tools
Aside from telling Google and Bing directly to index your site, it’s important to optimize internal links and continue growing your link building strategy to help search engines find your new pages on their own.
Source: Search Engine Journal
3 Google Display Network Targeting Facts
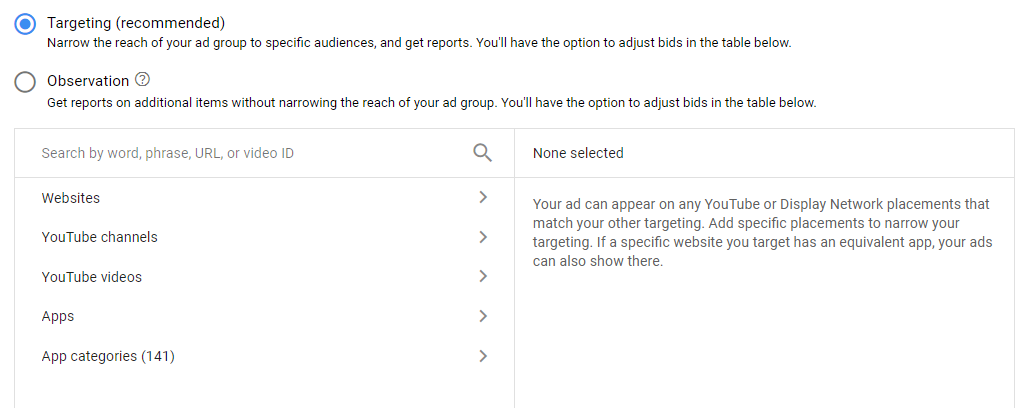
- Placements aren’t just websites – most advertisers think of the Display Network as a collection of websites where we can show ads. And while this is correct, it’s also important to remember that ads can also appear on YouTube channels, YouTube videos, relevant apps, and app categories. It’s also important to monitor your placement reports to ensure that your ads are showing up where you want them to.
- Keyword targeting can work in a couple of ways – when using keywords targeting you can choose from 2 keyword settings. The audience setting will show your ads to users who have an active interest in your selected keywords. The content setting uses contextual targeting to put your ads in front of the selected users. Meaning Google will take your list of keywords and try to find relevant websites or apps as placements.
- Google can help if you’re looking for audiences – utilize Google’s “ideas” tab in targeted audiences. Google can create custom intent audiences based on your remarketing lists, your Search campaigns, your user behavior, and more.
Source: Joe Martinez, WordStream




















